Remotes in GitLab
Last updated on 2025-12-12 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 45 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How do I share my changes with others on the web?
Objectives
- Explain what remote repositories are and why they are useful.
- Push to or pull from a remote repository.
Version control really comes into its own when we begin to collaborate with other people. We already have most of the machinery we need to do this; the only thing missing is to copy changes from one repository to another.
Systems like Git allow us to move work between any two repositories. In practice, though, it’s easiest to use one copy as a central hub, and to keep it on the web rather than on someone’s laptop. Most programmers use hosting services like GitHub, Bitbucket or GitLab to hold those main copies; we’ll explore the pros and cons of this in a later episode.
Let’s start by sharing the changes we’ve made to our current project with the world. To this end we are going to create a remote repository that will be linked to our local repository.
1. Create a remote repository
We are going to create a project and connect a local Git repository to it.
To create a project, we click on the button with the “+” symbol near the top of the side menu on the right and select “New project/repository”.
Multiple options are presented for how to create the new project. In this lesson we will only look at, and use, the first option: “Create blank project”. So click on that.
This leads to the following page:
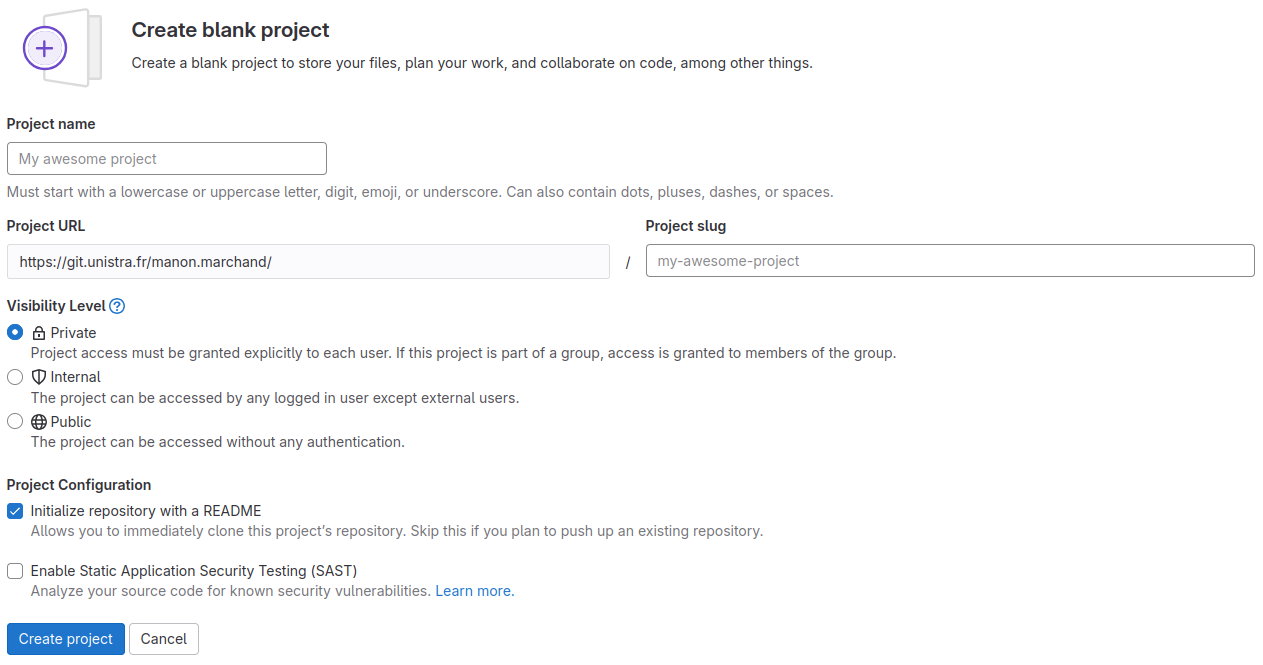
The “Project name” field is for just that, the project name. Its value has no other purpose and can be changed at anytime without indirect consequences (the direct consequence being, that its name will be different). We will call it “recipes”.
As we fill in the project name, a project slug gets suggested in the respective field. The project slug is the last part of the project’s, and the associated Git repository’s, URL or web address.
Project URL and Project Slug
The two fields under labels “Project URL” and “Project slug” are the only fields in this form for which changing the value later might cause problems. They determine the URL under which the project’s pages and the project’s Git repository can be found, so changing them later might brake links and bookmarks as well as connections from Git repositories on other systems, for example on contributors’ machines.
We ignore the field labeled “Project deployment target (optional)”.
The choice under label “Visibility Level” determines the project’s visibility.
Visibility
GitLab offers three settings for the visibility of a project: public, internal, and private. Publicly visible projects can be looked at by anyone that can access the GitLab instance, projects with internal visibility can be looked at by anyone logged in to the instance, while projects with private visibility can only be looked at by its members.
We choose “Private” for our project’s visibility.
Note: Since this repository will be connected to a local repository, it needs to be empty. Leave “Initialize this repository with a README” unchecked.
README
A project’s README file usually contains basic information about the project: what it contains, how it can be used (for example built or installed, if it is a software project), how to contribute, how to get help, and licensing information.
It is common to write README files in Markdown format, indicated by
the filename suffix .md.
Platforms like GitLab show the contents of a project’s README file on its homepage; if it is in Markdown format, in its rendered form.
Change Name, Description, Visibility, or Avatar
Click on the “Settings” sub-menu and select its “General” entry. Set the description to “Alfredo and Jimmy’s recipes.”.
The project description appears in many lists and on some pages under the project’s name.
Then change any of the project’s name, visibility, or avatar. Do not forget to click the “Save changes” button once you are done.
Markdown
Markdown is a markup language like HTML, on which the World Wide Web is based, or wikitext, which is used to write Wikipedia’s content. Its markup directives, indicating for example that something is a headline or a list item, are such that they serve their purpose even in the plain text form.
There are many variants (or flavors) of Markdown and GitLab has its own. Other than for rendering Markdown files in repositories on its web interface, GitLab allows for Markdown input in many of its interface’s text fields, such as issue descriptions or comments.
This effectively does the following on GitLab’s servers:
If you remember back to the earlier episode where we added and committed our
earlier work on guacamole.md, we had a diagram of the local
repository which looked like this:
Now that we have two repositories, we need a diagram like this:
Note that our local repository still contains our earlier work on
guacamole.md, but the remote repository on GitLab appears
empty as it doesn’t contain any files yet.
2. Connect local to remote repository
Now we connect the two repositories. We do this by making the GitLab repository a remote for the local repository. The home page of the repository on GitLab includes the URL string we need to identify it.
HTTPS vs. SSH
We use SSH here because, while it requires some additional configuration, it is a security protocol widely used by many applications. The steps below describe SSH at a minimum level for GitLab.
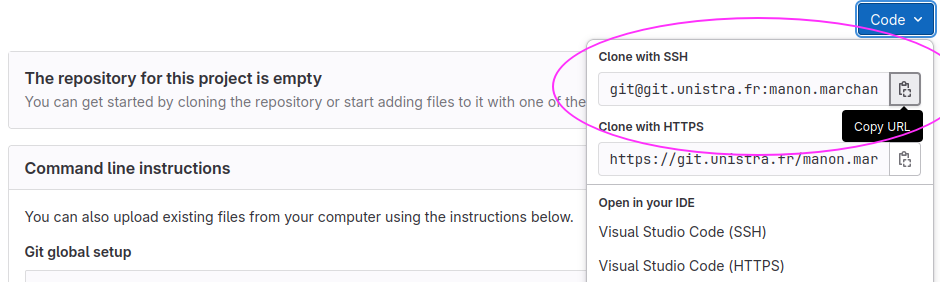
Copy that URL from the browser, go into the local
recipes repository, and run this command:
Make sure to use the URL for your repository rather than Alfredo’s:
the only difference should be your username instead of
alflin.
origin is a local name used to refer to the remote
repository. It could be called anything, but origin is a
convention that is often used by default in git and GitLab (and other
forges like GitHub), so it’s helpful to stick with this unless there’s a
reason not to.
We can check that the command has worked by running
git remote -v:
OUTPUT
origin git@git.unistra.fr:alfin/recipes.git (fetch)
origin git@git.unistra.fr:alfin/recipes.git (push)We’ll discuss remotes in more detail in the next episode, while talking about how they might be used for collaboration.
3. SSH Background and Setup
Before Alfredo can connect to a remote repository, he needs to set up a way for his computer to authenticate with GitLab so it knows it’s him trying to connect to his remote repository.
We are going to set up the method that is commonly used by many different services to authenticate access on the command line. This method is called Secure Shell Protocol (SSH). SSH is a cryptographic network protocol that allows secure communication between computers using an otherwise insecure network.
SSH uses what is called a key pair. This is two keys that work together to validate access. One key is publicly known and called the public key, and the other key called the private key is kept private. Very descriptive names.
You can think of the public key as a padlock, and only you have the key (the private key) to open it. You use the public key where you want a secure method of communication, such as your GitLab account. You give this padlock, or public key, to GitLab and say “lock the communications to my account with this so that only computers that have my private key can unlock communications and send git commands as my GitLab account.”
What we will do now is the minimum required to set up the SSH keys and add the public key to a GitLab account.
The first thing we are going to do is check if this has already been done on the computer you’re on. Because generally speaking, this setup only needs to happen once and then you can forget about it.
Keeping your keys secure
You shouldn’t really forget about your SSH keys, since they keep your account secure. It’s good practice to check your SSH keys every so often to ensure they are still secure, up to date, and that there are no unauthorized keys that could compromise your account. This is especially important if you are using multiple computers to access your account.
We will run the list command to check what key pairs already exist on your computer.
Your output is going to look a little different depending on whether or not SSH has ever been set up on the computer you are using.
Alfredo has not set up SSH on his computer, so his output is
OUTPUT
ls: cannot access '/c/Users/Alfredo/.ssh': No such file or directoryIf SSH has been set up on the computer you’re using, the public and
private key pairs will be listed. The file names are either
id_ed25519/id_ed25519.pub or
id_rsa/id_rsa.pub depending on how the key
pairs were set up. Since they don’t exist on Alfredo’s computer, he uses
this command to create them.
If you need to create an SSH key pair with a custom name or store it in a non-default location (e.g., because a default-named key like id_ed25519 already exists), Git may not automatically use it when pushing or pulling from GitLab.
One solution is to add a GitLab entry to your SSH config.
Open or create the SSH config file:
Add an entry for GitLab, replacing the path with your key’s actual name and location:
Host git.unistra.fr
HostName git.unistra.fr
User git
IdentityFile ~/<full_path_to_SSH_key_file>/<key_name>
IdentitiesOnly yesSave and exit. Now Git will use the correct key when pushing to GitLab.
3.1 Create an SSH key pair
To create an SSH key pair Alfredo uses this command, where the
-t option specifies which type of algorithm to use and
-C attaches a comment to the key (here, Alfredo’s
email):
If you are using a legacy system that doesn’t support the Ed25519
algorithm, use:
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
OUTPUT
Generating public/private ed25519 key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/c/Users/Alfredo/.ssh/id_ed25519):We want to use the default file, so just press Enter.
OUTPUT
Created directory '/c/Users/Alfredo/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):Now, it is prompting Alfredo for a passphrase. Since he is using his kitchen’s laptop that other people sometimes have access to, he wants to create a passphrase. Be sure to use something memorable or save your passphrase somewhere, as there is no “reset my password” option. Note that, when typing a passphrase on a terminal, there won’t be any visual feedback of your typing. This is normal: your passphrase will be recorded even if you see nothing changing on your screen.
OUTPUT
Enter same passphrase again:After entering the same passphrase a second time, we receive the confirmation
OUTPUT
Your identification has been saved in /c/Users/Alfredo/.ssh/id_ed25519
Your public key has been saved in /c/Users/Alfredo/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:SMSPIStNyA00KPxuYu94KpZgRAYjgt9g4BA4kFy3g1o a.linguini@ratatouille.fr
The key's randomart image is:
+--[ED25519 256]--+
|^B== o. |
|%*=.*.+ |
|+=.E =.+ |
| .=.+.o.. |
|.... . S |
|.+ o |
|+ = |
|.o.o |
|oo+. |
+----[SHA256]-----+The “identification” is actually the private key. You should never share it. The public key is appropriately named. The “key fingerprint” is a shorter version of a public key.
Now that we have generated the SSH keys, we will find the SSH files when we check.
OUTPUT
drwxr-xr-x 1 Alfredo 197121 0 Jul 16 14:48 ./
drwxr-xr-x 1 Alfredo 197121 0 Jul 16 14:48 ../
-rw-r--r-- 1 Alfredo 197121 419 Jul 16 14:48 id_ed25519
-rw-r--r-- 1 Alfredo 197121 106 Jul 16 14:48 id_ed25519.pub3.2 Copy the public key to GitLab
Now we have a SSH key pair and we can run this command to check if GitLab can read our authentication.
OUTPUT
The authenticity of host 'git.unistra.fr (192.30.255.112)' can't be established.
RSA key fingerprint is SHA256:nThbg6kXUpJWGl7E1IGOCspRomTxdCARLviKw6E5SY8.
This key is not known by any other names
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? y
Please type 'yes', 'no' or the fingerprint: yes
Warning: Permanently added 'git.unistra.fr' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
git@git.unistra.fr: Permission denied (publickey).Right, we forgot that we need to give GitLab our public key!
First, we need to copy the public key. Be sure to include the
.pub at the end, otherwise you’re looking at the private
key.
OUTPUT
ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIDmRA3d51X0uu9wXek559gfn6UFNF69yZjChyBIU2qKI a.linguini@ratatouille.frNow, going to git.unistra.fr, click on your profile icon in the top left corner to get the drop-down menu. Click “Preferences”, then on the settings page, click “SSH keys”, on the left side menu. Click the “Add new key” button on the right side. Now, you can add the title (Alfredo uses the title “Alfredo’s Kitchen Laptop” so he can remember where the original key pair files are located), paste your SSH public key into the field, and click the “Add key” to complete the setup.
Now that we’ve set that up, let’s check our authentication again from the command line.
OUTPUT
Welcome to GitLab, @alfredo!Good! This output confirms that the SSH key works as intended. We are now ready to push our work to the remote repository.
4. Push local changes to a remote
Now that authentication is setup, we can return to the remote. This command will push the changes from our local repository to the repository on GitLab:
Since Alfredo set up a passphrase, it will prompt him for it. If you completed advanced settings for your authentication, it will not prompt for a passphrase.
OUTPUT
Enumerating objects: 16, done.
Counting objects: 100% (16/16), done.
Delta compression using up to 8 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (11/11), done.
Writing objects: 100% (16/16), 1.45 KiB | 372.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 16 (delta 2), reused 0 (delta 0)
remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (2/2), done.
To https://git.unistra.fr/alflin/recipes.git
* [new branch] main -> mainProxy
If the network you are connected to uses a proxy, there is a chance that your last command failed with “Could not resolve hostname” as the error message. To solve this issue, you need to tell Git about the proxy:
BASH
$ git config --global http.proxy http://user:password@proxy.url
$ git config --global https.proxy https://user:password@proxy.urlWhen you connect to another network that doesn’t use a proxy, you will need to tell Git to disable the proxy using:
Password Managers
If your operating system has a password manager configured,
git push will try to use it when it needs your username and
password. For example, this is the default behavior for Git Bash on
Windows. If you want to type your username and password at the terminal
instead of using a password manager, type:
in the terminal, before you run git push. Despite the
name, Git
uses SSH_ASKPASS for all credential entry, so you may
want to unset SSH_ASKPASS whether you are using Git via SSH
or https.
You may also want to add unset SSH_ASKPASS at the end of
your ~/.bashrc to make Git default to using the terminal
for usernames and passwords.
Our local and remote repositories are now in this state:
The ‘-u’ Flag
You may see a -u option used with git push
in some documentation. This option is synonymous with the
--set-upstream-to option for the git branch
command, and is used to associate the current branch with a remote
branch so that the git pull command can be used without any
arguments. To do this, simply use git push -u origin main
once the remote has been set up.
We can pull changes from the remote repository to the local one as well:
OUTPUT
From git.unistra.fr:alflin/recipes
* branch main -> FETCH_HEAD
Already up-to-date.Pulling has no effect in this case because the two repositories are already synchronized. If someone else had pushed some changes to the repository on GitLab, though, this command would download them to our local repository.
GitLab GUI
Browse to your recipes repository on GitLab. Under the
Code tab, find and click on “Commits”. Hover over, and click on, the two
buttons to the right of each commit and on their commit message. What
information can you gather/explore from these buttons? How would you get
that same information in the shell?
The left-most button (with the picture of a clipboard) copies the
full identifier of the commit to the clipboard. In the shell,
git log will show you the full commit identifier for each
commit.
The right-most button lets you view all of the files in the
repository at the time of that commit. To do this in the shell, we’d
need to checkout the repository at that particular time. We can do this
with git checkout ID where ID is the identifier of the
commit we want to look at. If we do this, we need to remember to put the
repository back to the right state afterwards!
When you click on the commit message you’ll see all of the changes
that were made in that particular commit. Green shaded lines indicate
additions and red ones removals. In the shell we can do the same thing
with git diff. In particular,
git diff ID1..ID2 where ID1 and ID2 are commit identifiers
(e.g. git diff a3bf1e5..041e637) will show the differences
between those two commits.
Uploading files directly in GitLab browser
GitLab also allows you to skip the command line and upload files directly to your repository without having to leave the browser. If you click on “Code”, then “Repository” in the left menu, you’ll see “recipes/+” at the top of the page. You can chose the option “Upload file” in the list.
GitLab Timestamp
Create a remote repository on GitLab. Push the contents of your local repository to the remote. Make changes to your local repository and push these changes. Go to the repo you just created on GitLab and check the timestamps of the files. How does GitLab record times, and why?
GitLab displays timestamps in a human readable relative format (i.e. “22 hours ago” or “three weeks ago”). However, if you hover over the timestamp, you can see the exact time at which the last change to the file occurred.
Push vs. Commit
In this episode, we introduced the “git push” command. How is “git push” different from “git commit”?
When we push changes, we’re interacting with a remote repository to update it with the changes we’ve made locally (often this corresponds to sharing the changes we’ve made with others). Commit only updates your local repository.
GitLab License and README files
In this episode we learned about creating a remote repository on GitLab, but when you initialized your GitLab repo, you didn’t add a README.md or a license file. If you had, what do you think would have happened when you tried to link your local and remote repositories?
In this case, we’d see a merge conflict due to unrelated histories. When GitLab creates a README.md file, it performs a commit in the remote repository. When you try to pull the remote repository to your local repository, Git detects that they have histories that do not share a common origin and refuses to merge.
OUTPUT
warning: no common commits
remote: Enumerating objects: 3, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), done.
From https://git.unistra.fr/alflin/recipes
* branch main -> FETCH_HEAD
* [new branch] main -> origin/main
fatal: refusing to merge unrelated historiesYou can force git to merge the two repositories with the option
--allow-unrelated-histories. Be careful when you use this
option and carefully examine the contents of local and remote
repositories before merging.
OUTPUT
From https://git.unistra.fr/alflin/recipes
* branch main -> FETCH_HEAD
Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy.
README.md | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 README.md- A local Git repository can be connected to one or more remote repositories.
- Use the SSH protocol to connect to remote repositories.
-
git pushcopies changes from a local repository to a remote repository. -
git pullcopies changes from a remote repository to a local repository.
